Sock Merchant Solution in CPP | HackerRank | Sock Merchant HackerRank Solution in CPP | Sock Merchant Solution HackerRank | Sock Merchant Solution
John works at a clothing store. He has a large pile of socks that he must pair by color for sale. Given an array of integers representing the color of each sock, determine how many pairs of socks with matching colors there are.
For example, there are socks with colors . There is one pair of color and one of color . There are three odd socks left, one of each color. The number of pairs is .
Function Description
Complete the sockMerchant function in the editor below. It must return an integer representing the number of matching pairs of socks that are available.
sockMerchant has the following parameter(s):
- n: the number of socks in the pile
- ar: the colors of each sock
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the number of socks represented in .
The second line contains space-separated integers describing the colors of the socks in the pile.
Constraints
- where
Output Format
Return the total number of matching pairs of socks that John can sell.
Sample Input
9
10 20 20 10 10 30 50 10 20
Sample Output
3
Explanation
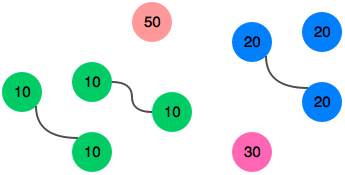
John can match three pairs of socks.
https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/sock-merchant/problem
Sock Merchant HackerRank Solution in CPP
Sock Merchant Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; vector<string> split_string(string); // Complete the sockMerchant function below. int sockMerchant(int n, vector<int> ar) { int pair=0; vector<bool> paired(n); fill(paired.begin(), paired.end(), false); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){ if(paired[i]==false&&paired[j]==false){ if(ar[i]==ar[j]){ pair++; paired[i]=paired[j]=true; } } } } return pair; } int main() { ofstream fout(getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")); int n; cin >> n; cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); string ar_temp_temp; getline(cin, ar_temp_temp); vector<string> ar_temp = split_string(ar_temp_temp); vector<int> ar(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int ar_item = stoi(ar_temp[i]); ar[i] = ar_item; } int result = sockMerchant(n, ar); fout << result << "\n"; fout.close(); return 0; } vector<string> split_string(string input_string) { string::iterator new_end = unique(input_string.begin(), input_string.end(), [] (const char &x, const char &y) { return x == y and x == ' '; }); input_string.erase(new_end, input_string.end()); while (input_string[input_string.length() - 1] == ' ') { input_string.pop_back(); } vector<string> splits; char delimiter = ' '; size_t i = 0; size_t pos = input_string.find(delimiter); while (pos != string::npos) { splits.push_back(input_string.substr(i, pos - i)); i = pos + 1; pos = input_string.find(delimiter, i); } splits.push_back(input_string.substr(i, min(pos, input_string.length()) - i + 1)); return splits; }



0 Comments